Patients’ data breaches happen often. According to Health IT Security, healthcare had 79% of all reported breaches in 2020 and the number of attacks against healthcare providers grew by 45% in January 2021. Such incidents lead to costly lawsuits and ruin patients’ lives. Not to mention the huge setbacks they mean for the organization. An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure–especially in the Healthcare IT world. That’s why you need to secure private data, rather than deal with the consequences of a successful attack.
As a report from Bitglass shows, 67.3% of breaches were caused by hacker attacks, and 21.5% by unauthorized disclosure. If the digital risks are that high then medical organizations need to be very serious about protecting their data.
What is an EMR System and why should it comply with HIPAA?
EMR stands for electronic medical records – health-related data. This information is collected and used by authorized medical staff within a healthcare organization. EMR systems are efficient tools for every healthcare provider as they introduce automation and improve workflow and service quality.
An EMR system is beneficial because it:
- Reduces errors caused by negligence (e.g., duplicate tests).
- Simplifies data transfer between patients and clinicians.
- Tracks patient data.
- Reminds users of ongoing procedures, vaccinations, and checkups.
- Automates appointments and staff scheduling.
- Reduce operational costs.
How are HIPAA and EMR connected?
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a legislative act protecting patient information in the USA. If you are a healthcare provider you are obliged to abide by this document. Under HIPAA, you must protect PHI (Personal Health Information) or ePHI (electronic PHI) which includes:
- demographics
- medical history
- mental health information
- lab results
- insurance information
All of this information is attached to each individual in an EMR. EMR compliance requirements are stated in Technical Safeguards of the HIPAA Security Rule.
Everyone who works with PHI must abide by HIPAA rules, including covered entities and business associates. Both traditional clinical services and telehealth services are governed by HIPAA.
What is considered a HIPAA violation?
- Illegally exposing ePHI to unauthorized parties, whether it was done intentionally or not.
- Not implementing necessary security protocols specified by the HIPAA Security Rule.
- Administrative or training protocols that do not meet requirements.
- Not notifying affected parties and public officials in case of data breaches.
- Not updatingimproving current gaps in compliance.
What are the risks of EMR noncompliance?
When it comes to healthcare, violation of confidentiality can result in damage to reputation and significant financial losses. Every party connected to your organization is liable to face penalties. Here are the main dangers you may face:
- ‘Meaningful Use’ Incentive programs – You may lose the benefits of Medical incentive programs if you do not meet all the privacy and security requirements.
- HIPAA and EHR violations – HHS can penalize you for noncompliance, even if no breaches took place! Violations might be reported by someone, or be uncovered in an official audit. Penalties may reach $1.5 million per violation!
- Lawsuits – If a breach occurs, you must inform affected patients as well as the media. Patients whose data was compromised, may file expensive lawsuits that will be in the courts for years.
It is a duty of every healthcare provider to ensure everyone from patients to stakeholders that you are able to protect ePHI.
HIPAA compliance checklist
There are particular steps you can take to comply with HIPAA:
- Create unified standards and procedures
Every healthcare organization needs a reliable administrative system to ensure the general HIPAA compliance requirements. Even the best technology won’t guarantee observance if your staff doesn’t know how to use it. You must train your employees how to use the system properly so they will not compromise personal data of patients. Your organization must have standards, policies, and procedures, which the workforce must strictly adhere to.
- Implement safeguards, both technical and physical
In terms of the HIPAA and security concerns of an EMR system, there are 2 types of protection required for patients’ data safety: physical and technical.
Physical safeguards are significant. Only authorized personnel should have access to the building where the data is stored. Security cameras and guards should secure the buildings and rooms containing the system’s computers and servers.
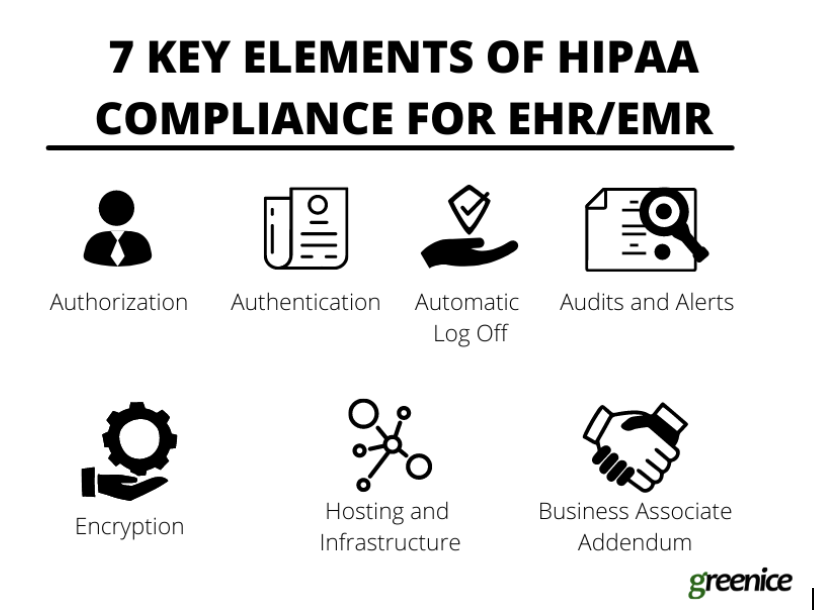
Technical safeguards – When implementing an EMR system, you must follow all the technical requirements and stick to the law. Here is a list of features you need to be compliant:
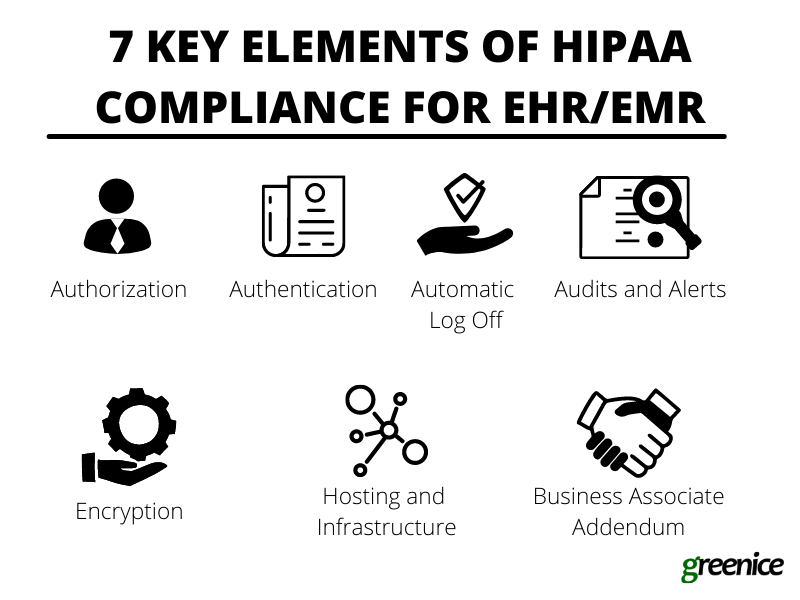
- Authorization – Data access must be cautiously administered so only necessary info is available to each employee (the Minimum Necessary rule). If medical staff have a personal assistant, this person should have permission to access only necessary data.
- Authentication – Every person who logs into the system must be verified. Only after the system authenticates the user, can they have access to the data.
- Automatic Log Off – After a certain period of inactivity the session should be automatically terminated. This feature prevents unauthorized access.
- Audits and Alerts – Every user’s activity should be monitored. This will allow the identification of suspicious activity.
- Encryption – Encryption helps protect the data during transfer. While not mandatory under HIPAA, encryption is highly recommended to maintain the absolutely safe transfer of data.
- Hosting and Infrastructure – You need to make sure that the hosting and infrastructure you are using to store patient data is safe and complies with HIPAA. The servers have to be protected both physically and technically. This can be achieved both in-house and with the use of 3rd party cloud solutions that comply with HIPAA (e.g. AWS and Google Cloud).
- Business Associate Addendum – BAA is a contract you sign with the 3rd party service provider who will have access to patients’ personal data. For instance, if you hire a web development company to build and maintain your EMR system, you will need to sign a BAA with them.
- Regular HIPAA risk assessment
By evaluating risks and analyzing the level of security in your organization, you can keep on top of any potential problems. You will be able to strengthen your system and eliminate any issues that cause trouble. Regular inspections include:
- Identifying where data is stored
- Identifying potential threats
- Analyzing security measures for PHI and the potential impact of a breach
- Documenting steps necessary to improve PHI protection
- Report data breaches if they occur
According to the Breach Notification Rule, if personal data is compromised, you are mandated to inform every party affected. A breach might mean unauthorized (non-compliant) access, acquisition, use, or disclosure of PHI. Notifications must be sent to individuals, the media, and to the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services. If an organization doesn’t follow proper procedures, major financial penalties can be levied as punishment.
- Analyze cases of violations and solve them
A HIPAA violation means disclosure of a patients’ private data due to lack of protection inside the healthcare organization. Every violation will be investigated, and penalties range from $100 to $50,000 depending on many factors (malicious intent, degree of negligence, number of compromised files, potential risks). After an incident, you must also have a plan of action to reestablish compliance.
- Document everything
The measures taken to restore compliance, every affected party, and the details of the violation – all must be documented. Every procedure, agreement, and plan is to be documented even if there is no issue taking place. Failure to provide such documentation will result in your company being non-compliant with the requirements of HSS OCR audit.
How to Apply This to Your Practice
HIPAA violations are dangerous not only for patients, but also for everyone responsible for handling patient data. Data must be protected using a secure EMR system. The following features will insure compliance with HIPAA requirements:
- authorized data access
- automatically terminated sessions
- activity monitoring and alerts
- data encryption
- HIPAA compliant servers and infrastructure
- BAA contract
Whether buying off-the-shelf, or developing custom healthcare solutions, make sure they are compliant with HIPAA and you’ll be fine, not fined.