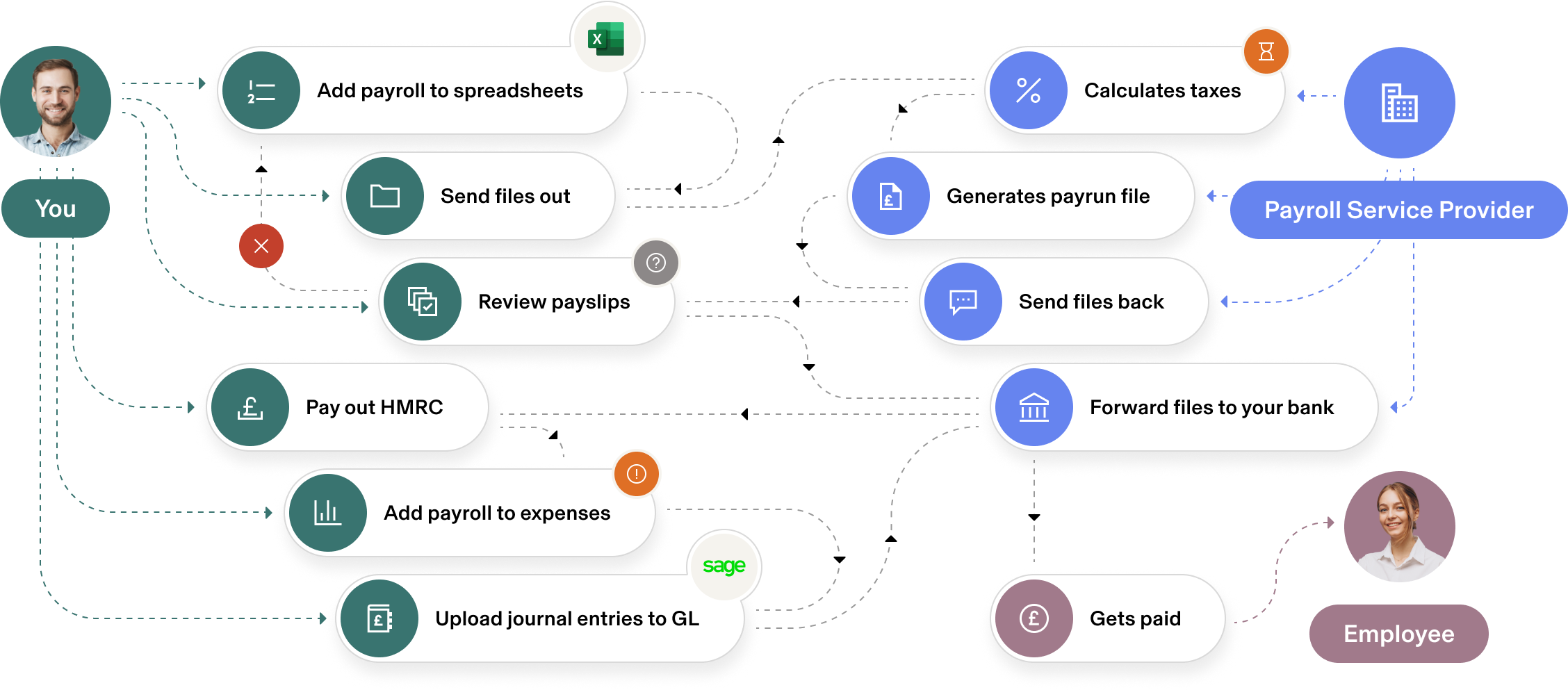
Payroll is an important function in every organization, and one that can lead to disputes with employees and the prevailing legislation. To avoid these disputes, organizations must ensure payroll compliance to prevailing federal, state, and local laws. Also, they must be in conformance with the agreements signed with employees on the promised benefits, provided they comply with the laws.
This is where payroll compliance tools help, as they automate tax calculations, manage employee classifications, and generate reports for compliance. Using this software, an organization can also sign agreements that don’t violate these provisions.
Components of Payroll Compliance
Payroll compliance consists of many components, each of which plays an important role in ensuring compliance with federal and state laws. Below are the key components of payroll compliance.
Employee Classification
As a first step, organizations must distinguish between full-time employees, part-time workers, and independent contractors. Employees are subject to payroll taxes, benefits, and labor protections, while independent contractors handle their own taxes and benefits. Misclassification can lead to tax penalties, lawsuits, and fines from agencies like the IRS and the Department of Labor. Businesses should regularly review job roles and use IRS guidelines, such as the “right to control” test, to determine classification.
Minimum Wage and Overtime Laws
Employers must comply with the federal minimum wage set by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), which is currently $7.25 per hour, unless a state or local law requires a higher rate. Some cities and states have increased the minimum wages, which means businesses must adjust payroll accordingly.
Overtime laws also play a key role in payroll compliance, as non-exempt employees must receive 1.5 times their regular pay for hours worked beyond 40 per week. Failing to comply can result in wage disputes, lawsuits, and penalties from the Department of Labor.
Taxation and Reporting
Payroll compliance requires accurate withholding and reporting of federal, state, and local taxes. Employers must deduct Social Security and Medicare (FICA) taxes, federal and state income taxes, and unemployment taxes (FUTA/SUTA) from employee wages. Inaccurate withholding or late tax payments can lead to financial penalties. Employers must also file payroll tax reports periodically with the IRS and state tax agencies. Forms like W-2s (for employees) and 1099s (for contractors) must be issued annually for proper tax documentation.
Payroll Record Keeping
Maintaining accurate payroll records is a legal requirement under the FLSA. Employers must keep records of wages, hours worked, tax withholdings, and benefits for at least three years. These records are necessary for audits, resolving disputes, and demonstrating compliance with wage and tax laws. Digital payroll software can help businesses store and organize records efficiently. Moreover, they can be retrieved during audits or employee inquiries.
Benefits and Deductions
Payroll compliance also includes managing employee benefits and deductions correctly. Businesses must accurately calculate and deduct contributions for health insurance, retirement plans like 401(k) contributions, and other voluntary benefits. Additionally, employers must process legally required deductions, including child support payments, wage garnishments, and union dues. Failure to withhold and remit these deductions on time can result in legal and financial consequences.
Multi-state and Global Compliance
Businesses operating in multiple states or countries must adhere to varying payroll regulations, tax laws, and employment policies. Each state in the U.S. may have different wage laws, tax rates, and leave policies, making payroll processing complex. For global businesses, additional challenges include currency conversions, tax treaties, and foreign labor laws. Employers must comply with all relevant regulations to avoid fines and employee disputes.
As you can see, there are many components to payroll compliance, and even small missteps can have serious consequences. This is why many organizations use payroll compliance software to automate these calculations and even file directly with the IRS and state departments.
What is Payroll Compliance Software?
Payroll compliance software is a digital solution that simplifies payroll calculations, tax withholdings, and benefits deductions while reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
Modern payroll compliance tools integrate with HR and accounting systems, ensuring seamless data flow and compliance with local, state, and federal regulations. They also assist in generating payroll reports, filing tax forms, and maintaining accurate employee records.
Some key features to look for in any payroll compliance software are:
- Automated payroll processing.
- Accurate tax calculations.
- Automated tax filing.
- Updated regulatory compliance.
- Employee classification and management.
- Payroll reporting and auditing.
- Time and attendance reporting.
- Data security.
Let’s now look at the best payroll compliance tools.
1. ADP
ADP is one of the leading payroll compliance providers that works well for businesses of all sizes. Its many features help businesses handle payroll and HR challenges.
Source: ADP
Key Features
- Offers full-service payroll services, from handling calculations to making direct deposits and filing taxes.
- Supports HR services like background checks, performance tracking, employee handbooks creation, and more.
- It comes with an employee self-service portal, using which employees can check their payroll details.
- Has a well-developed mobile app to schedule shifts, approve time-off, and more.
- Automatically includes changes to taxation rules.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Scalable.
- Extensive customer support.
- Multi-jurisdictional payroll services.
Cons:
- More features require higher plans.
- Requires expertise for setup.
Contact customer service for a quote.
2. Quickbooks Payroll
Intuit Quickbooks is also a popular tool for processing payroll, making deposits, and even filing taxes automatically. It can save a ton of time and effort with its features to track time and manage other HR functions.
Source: QuickBooks
Key Features
- Offers tax penalty protection, under which Intuit will pay $25,000 if you receive a payroll penalty after using QuickBooks.
- Helps businesses pay employees and contractors on schedule.
- Reduces manual entries.
- Manages time tracking.
- Integrates accounting data with payroll for streamlined insights.
Pros:
- Comes with a mobile app for easy access.
- 24/7 support.
- E-files unlimited 1099s.
- Saves time and effort.
Cons:
- Limited international support.
- Customer support can be slow during peak times.
3. Gusto
Gusto is a payroll and HR compliance solution designed specifically for small and medium businesses. Besides being affordable, it is easy to use and provides deep insights into payroll tracking and expense management.
Source: Gusto
Key Features
- Handles accurate time tracking to save headaches for HR managers.
- Stays on top of employee performance and makes appropriate calculations.
- Creates reports to provide the required insights about expenses and employee data for informed decision-making.
- Supports payroll processing for remote teams.
- Includes health insurance administration.
Pros:
- Intuitive interface.
- Strong payroll compliance.
- Benefits administration.
- Automated tax filing.
Cons:
- Limited features for large enterprises.
- Limited international payroll support.
4. Paychex
Paychex is a well-known payroll compliance software that’s suited for businesses of all sizes and industries. Its features ease payroll processing while helping you stay compliant with existing regulations.
Source: Paychex
Key Features
- Handles payroll calculations and tax deductions.
- Automatically files taxes for both employees and contractors at the federal, state, and local levels.
- Includes benefits like health insurance, retirement, and workers’ compensation.
- It comes with an employee self-service portal.
- Sends alerts in case of changes to labor laws.
Pros:
- Scalable for businesses of all sizes.
- Integrates HR and benefits administration.
- Advanced reporting and analytics.
- Accurate processing.
Cons:
- Some features can cost extra.
- Too complex for solopreneurs and small businesses.
5. Rippling
Rippling is a comprehensive platform that combines HR, IT, and finance systems to automate payroll processing. It is well-suited for processing payrolls across multiple jurisdictions and countries.
Source: Rippling
Key Features
- Offers Employer of Record (EOR) services to manage international employees.
- Integrates well with more than 500 apps
- It comes with a well-developed dashboard that provides all the insights you need.
- Automate HR, payroll, and IT systems to eliminate manual data entry.
- Updates tax rules and workflows based on regulatory changes.
Pros:
- Highly scalable.
- Comprehensive.
- Global payroll support.
- Extensive automation.
Cons:
- Initial set up can be time-consuming.
- No free trial.
6. Middesk
Middesk is a specialized tool for streamlining payroll calculations in different states. It can also handle multi-state employees and hiring to meet your talent needs. Middesk takes care of withholding and unemployment payroll registrations to meet state and federal regulations.
Source: Middesk
Key Features
- Automates the creation of accounts based on each state’s requirements.
- Tracks regulatory changes and updates processes to meet them.
- It comes with a centralized dashboard to manage all accounts.
- Integrates with many systems through its APIs.
- Takes care of all aspects of payroll processing.
Pros:
- Ideal for businesses looking to expand into more regions.
- Automates repetitive tasks.
- Reduces the chances of fines and penalties.
- Handles state tax registration.
Cons:
- More suited for companies operating across states.
- Focuses largely on payroll processing only.
Get in touch with the sales team.
7. CorpNet
CorpNet helps businesses to handle payroll taxes and processing across all the states. This platform also calculates the State Income tax (SIT) and the State Unemployment Insurance Tax (SUIT) for every state.
Source: CorpNet
Key Features
- Centralizes access to important documents like annual reports and tax filing.
- Sends reminders for the due dates to help you stay on top always.
- It can legally represent you across the 50 states for tax-related cases.
- Offers extensive services for setting up a business and meeting regulatory requirements beyond just taxation.
Pros:
- Multi-state jurisdictions.
- Expert guidance.
- Supports business expansion.
- Affordable pricing
Cons:
- More focus on business services.
- Does not support the complete payroll processing cycle.
Now that you know the best payroll compliance platforms, let’s quickly look at how to select the right one for your business requirements.
How to Select the Right Payroll Compliance Platform?
To select the right payroll compliance software, here are some factors to consider.
Regulatory Compliance Support
The platform you choose should help businesses stay compliant with federal, state, and local payroll regulations. It must update automatically to reflect changes in tax laws, wage laws, and reporting requirements. If you operate internationally, it must also support global payroll compliance.
Tax Filing and Payment Automation
A good payroll compliance tool should automate tax calculations, deductions, and filings. Look for features that handle payroll tax payments, generate necessary forms like W-2s and 1099s, and prevent tax penalties. It is also helpful if the tool can e-file forms on your behalf.
Integration Capabilities
The selected payroll compliance software should integrate seamlessly with your accounting, HR, performance management, and time-tracking systems. This integration prevents errors and simplifies payroll processing by syncing data across platforms. If you have many custom systems, look for platforms that offer APIs for custom integration.
Scalability for Business Growth
A platform should accommodate business expansion – whether it is hiring new employees, entering new states, or managing multiple payroll schedules. Look for tools that support multi-state payroll and compliance tracking.
Data Security and Compliance Certifications
Payroll data contains sensitive employee information, so the software must have strong security measures, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with SOC 2 or ISO 27001 standards.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
The interface should be user-friendly, allowing HR teams or business owners to navigate payroll compliance tasks without extensive training. Cloud-based access can also be beneficial for remote management.
Cost and Value
Pricing models vary. Some platforms charge per employee, per month, while others have flat fees. Consider the cost against the features provided and ensure you’re not paying for unnecessary functionalities.
With these factors, you can zero-in on the platform that best fits your payroll requirements.
Final Thoughts
Payroll compliance is an important part of business operations, as it ensures that employees are paid correctly while companies meet tax and labor law requirements. The right payroll compliance software simplifies complex regulations, automates tax filings, and reduces the risk of errors or penalties. When selecting a tool, focus on compliance support, automation capabilities, integration options, scalability, security, ease of use, and cost. Whether opting for a comprehensive payroll solution or a specialized compliance tool, the key is to choose a platform that meets your specific needs. We hope the tools discussed in this article can help you make the right investments in payroll compliance platforms.