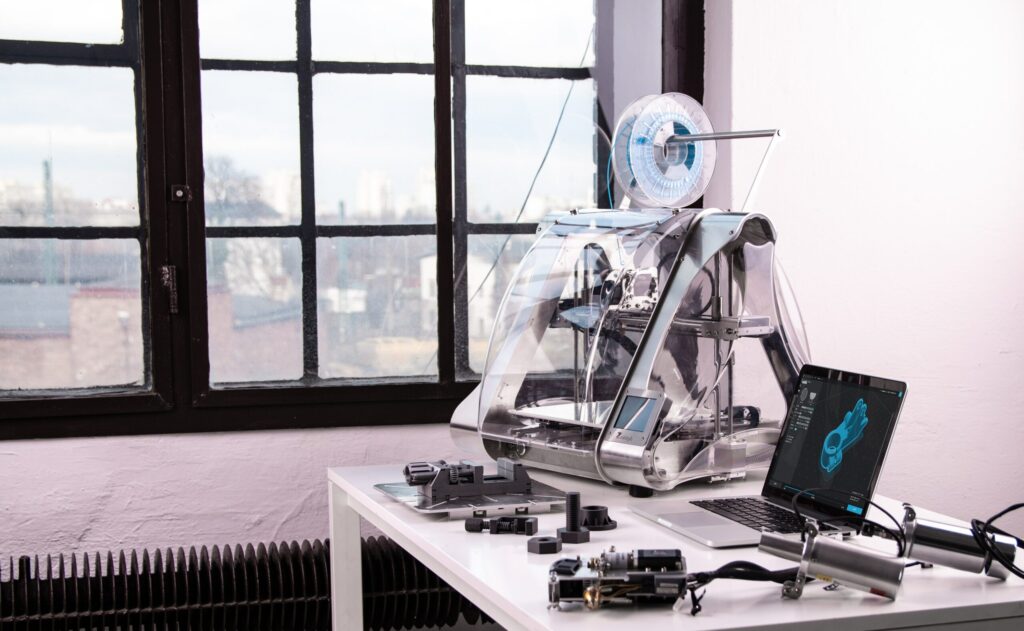
Rapid manufacturing primarily involves directly creating products and components using additive manufacturing methods. It differs from traditional manufacturing practices because its modus operandi is not formative or subtractive, as with machining or molding.
Instead, rapid manufacturing techniques are additive in how they layer up parts during production.
The Different Types of Rapid Manufacturing
It’s imperative to know that rapid manufacturing is an umbrella term that includes rapid prototyping, rapid tooling, and related technologies.
- Rapid prototyping is a fascinating and relatively novel technology for fast-developing physical models and fully functional prototypes directly from CAD-made models.
- Rapid tooling mostly involves the creation of tooling used while manufacturing products and components by rapid prototyping.
Together, they create the rapid manufacturing system, which is widely used for releasing intricate designs while shortening the time-to-market of outputs and is regarded as competitiveness-enhancing technology.

Photo by Kumpan Electric from Unsplash
Since the mid-1980s, when rapid prototyping was first introduced by 3D Systems’ Founder Chuck Hull, many experiments have been done, and different additive manufacturing technologies have emerged.
Nowadays, various methods can be used in rapid prototyping and rapid manufacturing to deposit the material for creating a proto-model through a particular rapid prototyping technique.
Most Used Rapid Manufacturing Techniques
Presently, the most widely used rapid manufacturing techniques in industries include 3D printing, stereolithography, selective laser sintering (SLS), and fused deposition modeling. However, rapid manufacturing is a continuously evolving technology, so rest assured that we haven’t seen everything yet.
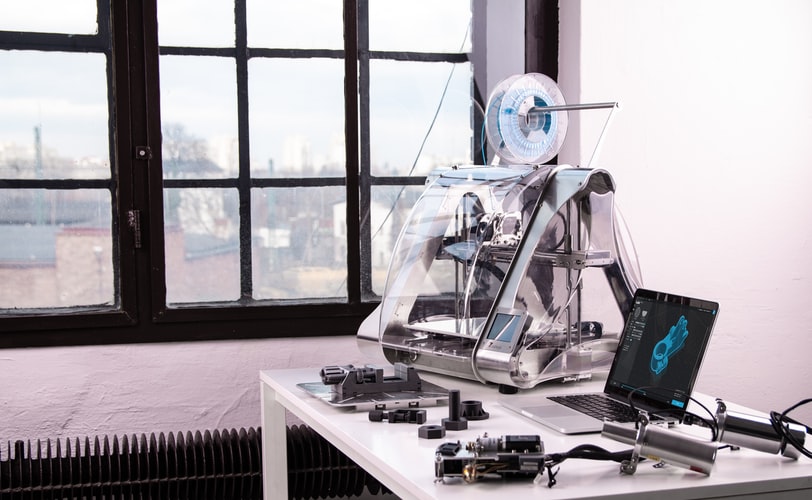

Photo by ZMorph All-in-One 3D Printers from Unsplash
Rapid prototyping models are becoming used more in industrial areas. Rapid manufacturing now satisfies the need for many purposes, from developing test prototypes with material attributes familiar to production parts to manufacturing models for medical applications.
Suppose you’re interested to know more about how this additive manufacturing method is utilized within modern-day industries and its application. In that case, we encourage you to read along and broaden your horizons.
Functional Applications Of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping and rapid tooling, as the core parts of rapid manufacturing, apply to many technologies and materials, making it an incredibly versatile technique that can be employed for multiple applications. The most famous functional applications of this technology include the creation of:
Concept Models
The concept models of future products allow designers to validate their ideas and their presumptions.
Additionally, a physical concept model is a fantastic way to explore the initial concept and demonstrate its validity to board members, clients, or investors to understand and approve the development of the product and create communication around it.

Photo by ThisIsEngineering from Pexels
Functional Prototypes
Functional prototypes permit engineers, developers, and designers to grasp the details that provide a precise image of the finished product by allowing them to verify its validity before it moves on to the next stage.
Prototypes are great because the product’s design, fit, manufacturability, and function should be tested before moving into full production mode, a considerably more expensive process.
Proving that a functional prototype will also be economically feasible to manufacture is another crucial part that rapid prototyping makes possible.
Having a first-rate functional prototype that achieves a delicate balance of functionality and aesthetics while being cost-effective is possible with these techniques.
Industrial Applications Of Rapid Manufacturing Technologies
Rapid manufacturing technologies offer the potential to significantly reduce the time required from the initial conceptualization of the product to putting the final version of that product on the shelves of global retail points.
Together with their abilities to enhance and improve product development, numerous industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, jewelry, coin making and more successfully use rapid manufacturing technologies.
Without further ado, here are some of the most notable industrial applications of rapid manufacturing technologies.
Medical Industry
- Rapid prototyping is widely used for surgery planning, diagnosis, training, and custom implant design and manufacture.
- 3D computer-aided design and manufacturing are also used to design and develop new medical products. They shorten the time to market and help further in research.
- The conversion of MRI results or CT scans, which are taken as input and later converted into CAD files, analyzes those files with CAM software’s help to produce specific products with rapid prototyping.
- The physical models permit correct identification of bone abnormality and intuitive understanding of anatomical issues for surgeons and implant designers.
Photo by Tom Claes from Unsplash
Mechanical Engineering
- Rapid prototyping is massively used in mechanical engineering to form and fit large mechanical models.
- It provides ease in the flow analysis and helps identify stress concentration points.
- Functional prototypes are often used as proof of concept and visualization.
- Rapid prototyping finds wide application in the automotive and aerospace industry.
Electronics
- Nearly all household electrical appliances are manufactured using rapid manufacturing technologies.
- Rapid prototyping and rapid tooling are beneficial for manufacturing specific futuristic contours in present-day electrical items.
In Footwear Designing
- The footwear for ultimate human comfort is achieved through the rapid prototyping technique.
- 3D printer-constructed footwear is lightweight yet stronger than the conventionally built one.
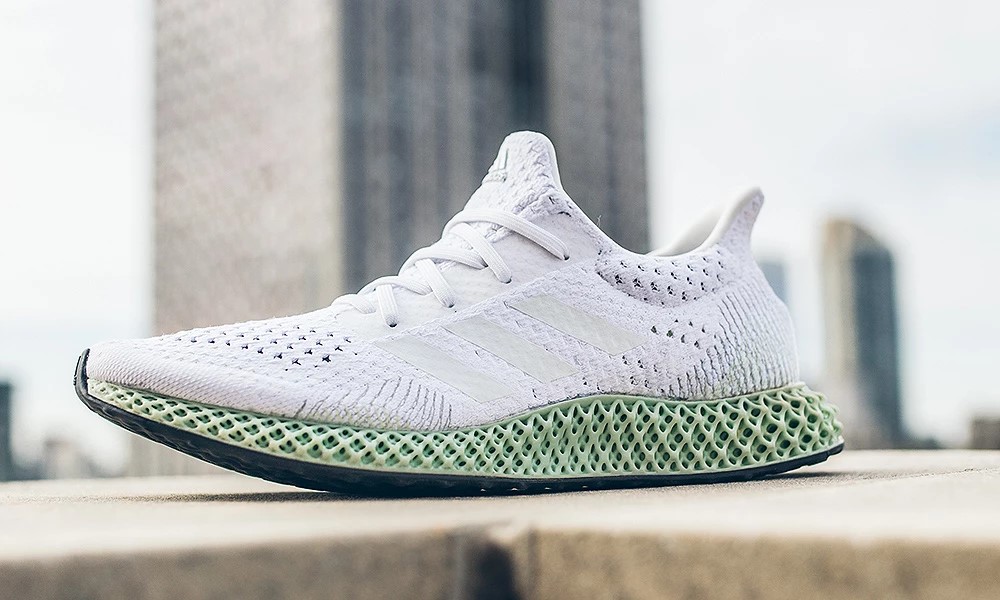

Photo from Fabbaloo
Final Thoughts
Rapid manufacturing technologies are one of the fastest-growing manufacturing technologies of our time. They allow product designers, developing teams, and mechanical engineers to visualize complex shapes that are not easily seen on connectional drawings and verify their concept ideas.
Furthermore, rapid prototyping and rapid tooling can be used in early or later design stages to build a conceptual model or alter the details before the prototype goes into mass production.
And even though these technologies have already proven their worth to numerous industries, expect rapid prototyping to become a manufacturing method used routinely by many design teams. Also, in conjunction with conventional manufacturing methods to scale models and mechanical parts even further.
